
LTE Explained
LTE-M
LTE-M is a cellular technology specifically designed for the needs of applications targeting the Internet of Things (IoT) or machine-to-machine (M2M) communications.What is LTE-M?
LTE-M is a low‑power wide‑area (LPWA) air interface that lets you connect IoT and M2M devices with medium data rate requirements. It enables longer battery lifecycles and greater in‑building range, as compared to standard cellular technologies such as 2G, 3G, or higher LTE categories.Key features include:
- Full mobility and in-vehicle hand-over
- Low power consumption
- Extended in-building range
- Support of voice functionality via VoLTE
Evolution from LTE Cat M1 to LTE Cat M2
LTE-M was first introduced as LTE Cat M1 in the 3GPP Release 13 standard that also defined Narrowband IoT (NB‑IoT or LTE Cat NB1) – both are LPWA technologies in the licensed spectrum. With 3GPP Release 14, the LTE Cat M2 standard has been set. While LTE Cat M1 transmitted data at a bandwidth of 1.4 MHz, LTE Cat M2 will increase to 5 MHz. It will bring improvements in several areas:- Data rate: LTE Cat M1 can support uplink and downlink speeds of 375 kb/s in half duplex mode, making it ideal for many IoT applications with low to medium data rate needs. LTE Cat M2 will increase data throughput to peak rates of 2.4 Mb/s for downloads and 2.6 Mb/s for uploads, broadening the appeal of LTE-M even for relatively high data speed applications such as video surveillance. At these speeds, it will also be much faster to deliver remote firmware updates over‑the‑air (FOTA) within reasonable timeframes and limiting drain on the battery. U-BLOX supports FOTA updates utilizing LWM2M (lightweight M2M), a light and compact protocol ideal for IoT applications.
- Mobility: As compared to NB‑IoT, LTE-M is ideal for mobile use cases, because it handles hand‑over between cell towers much like high-speed LTE. For example, if a vehicle moves from point A to point B crossing several different network cells, an LTE-M device would behave the same as a cellular phone and never drop the connection. An NB‑IoT device, on the contrary, would have to re‑establish a new connection at some point after a new network cell is reached. Release 14 LTE-M now brings several benefits over the mobility features already supported in Release 13 LTE-M. These include less power consumption for mobile applications and full mobility (intra and inter-frequency).
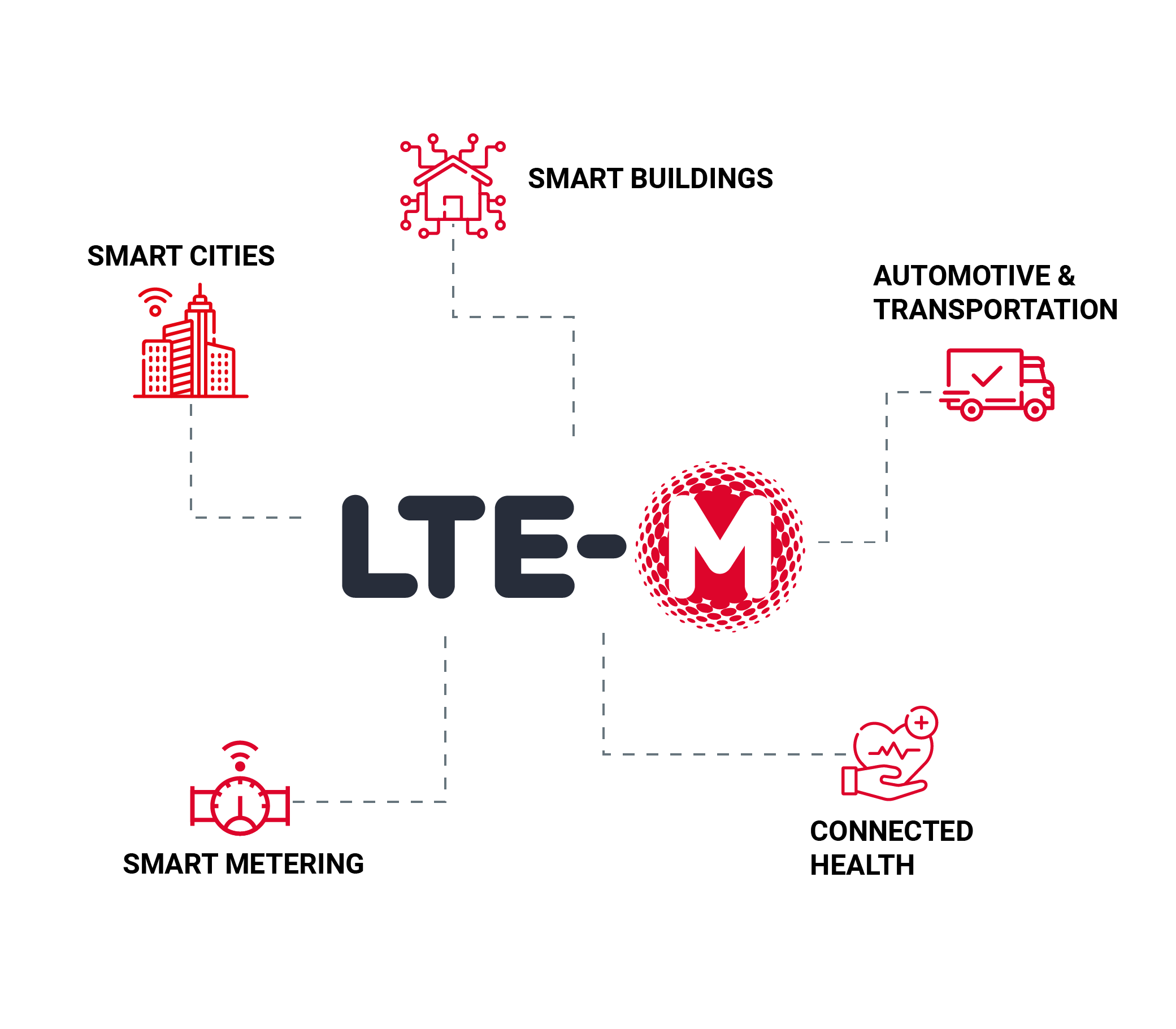
Key Applications
Automotive & transportation
LTE-M supports full hand-over between network cells from a moving vehicle and is therefore well-suited for mobile use cases with medium data rate needs, such as vehicle tracking, asset tracking, telematics, fleet management and usage-based insurance.
Smart metering
LTE-M is also ideal for monitoring metering and utility applications via regular and small data transmission. Network coverage is a key issue in smart metering rollouts. Since meters are commonly located inside buildings or basements, LTE-M’s extended range leads to better coverage in hard-to-reach areas.
Smart buildings
Connected health
Smart cities
Celebrating a decade of excellence: Airmax Remote renews ISO 9001:2015 accreditation
We are delighted to announce that Airmax Remote has successfully renewed our ISO 9001:2015 accreditation for the supply of advanced telematics and vehicle diagnostic systems within the UK. This year marks a significant milestone as we celebrate 10 years of continuous certification under this internationally recognised standard, underscoring our solemn commitment to diligence, regulatory conformance, quality and excellence.
Airmax Remote becomes signatory to The Police Industry Charter
This March, AirMax Remote proudly became one of the founder signatories to The Police Industry Charter, a landmark initiative spearheaded by BlueLight Commercial alongside key stakeholders such as the NPCC, APCC, RISC, the Home Office and the Office of the Police Chief Scientific Adviser.
Airmax Remote Ltd to showcase its advanced fleet telematics solutions at the 49th NAPFM event
Airmax Remote Ltd, a leading provider of advanced fleet telematics solutions for the emergency...




